Five faculties at the University of Basel are welcoming new professors to their ranks.
Cancer treatments often cause nerve damage that can lead to long-lasting symptoms. Medication has proven ineffective in these cases. A sports scientist at the University of Basel, together with an interdisciplinary team from Germany, has now shown that simple exercises can prevent nerve damage.
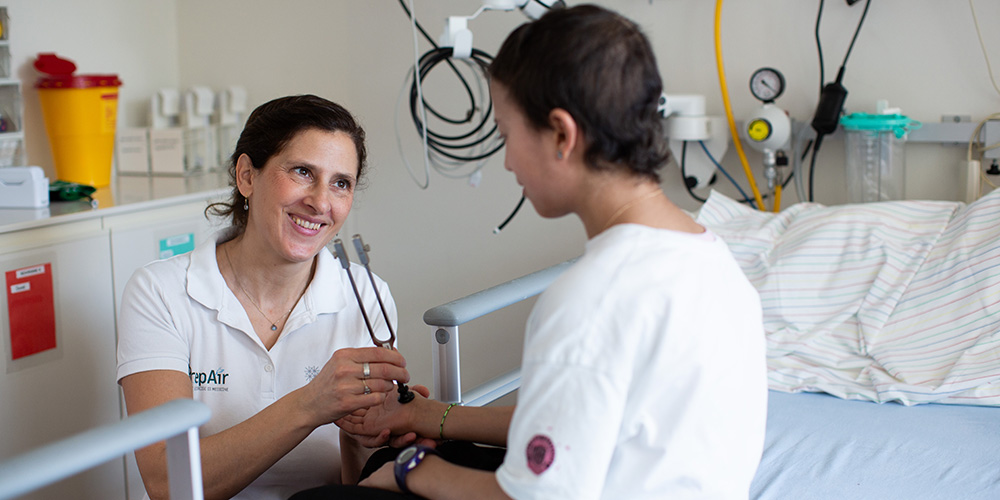
Prof. Dr. h.c. mult. Andrea Schenker-Wicki, President of the University of Basel and Eucor—The European Campus, was awarded an honorary doctorate by the Université de Haute-Alsace.

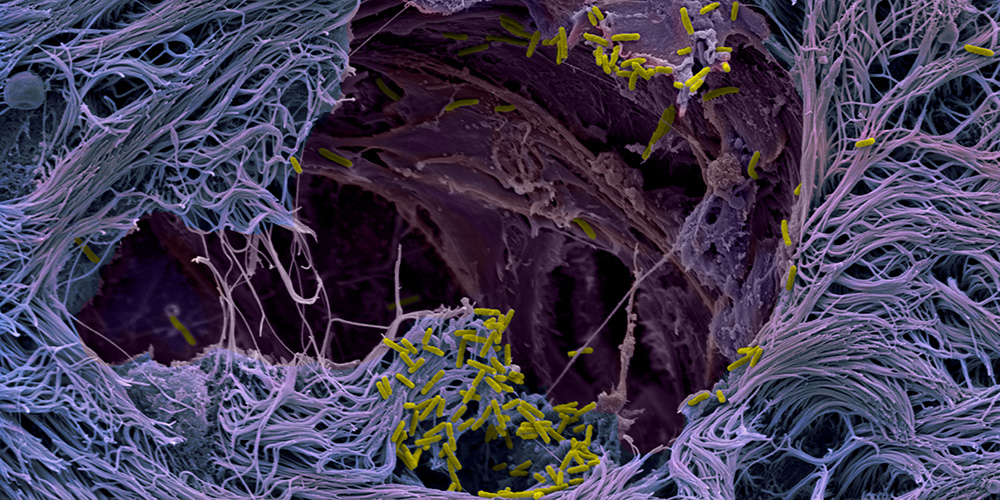
How do pathogens invade the lungs? Using human lung microtissues, a team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has uncovered the strategy used by a dangerous pathogen. The bacterium targets specific lung cells and has developed a sophisticated strategy to break through the lungs’ line of defense.
Dense settlement on one side, nature on the other. When space is short, we need to think hard about how to use it. What are the important criteria here? A historian from the University of Basel is writing a doctoral thesis on the fads and social development that have influenced green spaces in urban planning.

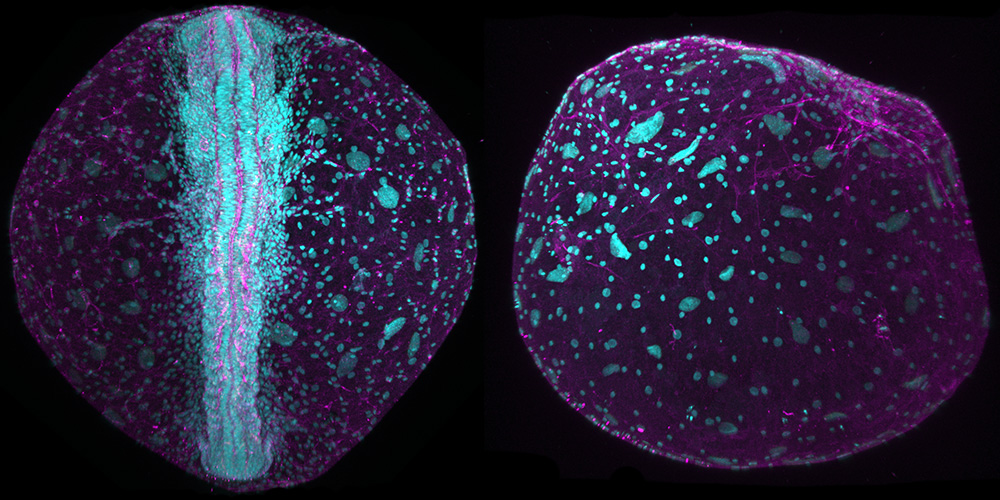
The annual killifish lives in regions with extreme drought. A research group at the University of Basel now reports in "Science" that the early embryogenesis of killifish diverges from that of other species. Unlike other fish, their body structure is not predetermined from the outset. This could enable the species to survive dry periods unscathed.
Bronze cauldrons were used by the inhabitants of the Mongolian steppe around 2,700 years ago to process animal blood and milk. This is shown by a protein analysis of archaeological finds from this period.

Lesbian, gay and bisexual people experience greater exclusion than heterosexual people. This is the conclusion of a recent study by researchers from the University of Basel and the University of Kaiserslautern-Landau (RPTU). Heterosexual individuals who deviate from traditional gender roles are also affected.

An estimated one-fifth of the world's population is affected by pollen allergies. Researchers at Swiss TPH and the University of Basel have now discovered that a high concentration of pollen can increase blood pressure in allergy sufferers.