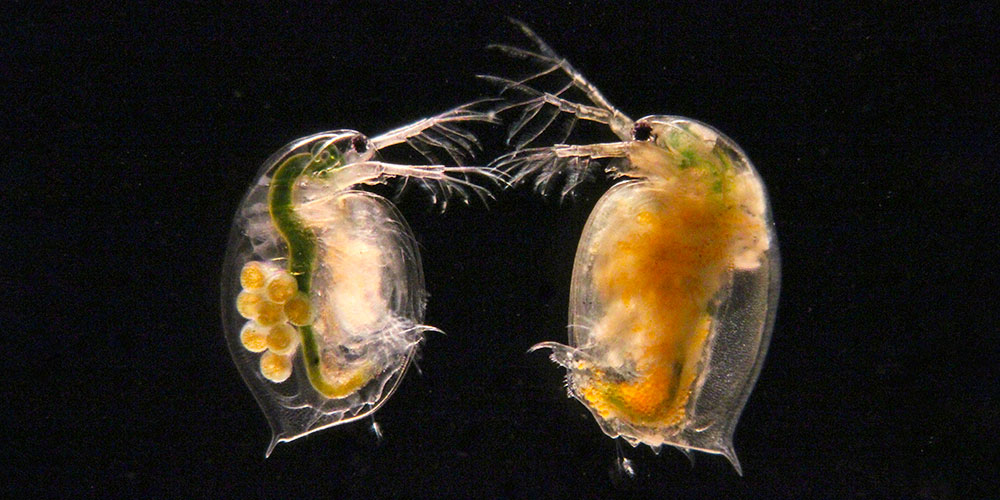
Competition over millions of years preserves genetic diversity
Variations in genetic material allow the water flea to defend itself against parasites, forcing the parasites to adapt. This coevolutionary loop has been running for at least 15 million years, as researchers at the University of Basel have demonstrated.
30 July 2024 | Yvonne Vahlensieck
Hosts and their parasites are in constant competition. Through genetic diversity, the host can change in such a way that infection is no longer possible. However, the parasite adapts quickly – and the game starts all over again. This is also referred to in evolutionary biology as the “Red Queen model” after the character in the book Alice in Wonderland who keeps running without getting anywhere.
These processes can occur without interruption over many millions of years, as a research group at the Department of Environmental Sciences at the University of Basel has now reported in the journal Nature Communication. This is a much longer period than previously thought. For the study, the team led by Professor Dieter Ebert compared the genetic material of millimeter-sized water fleas infected by a parasitic bacterium.
The parasite penetrates the intestines of the water flea, where it attaches itself to the mucus layer. The water flea can ward off infection by altering the molecules that are fixed on the surface of this mucus. The parasite then adapts its own surface to the altered mucus structure and is briefly in the lead again. This process of coevolution ensures that multiple genetic variants for surface molecules are always preserved in the water flea without one ever prevailing.
Looking even deeper into the past
So far, the researchers have been able to trace this coevolution between the water flea and the parasite back to before the last ice age, around 100,000 years ago. “Now we have taken another giant leap forward and have been able to show that the process goes back at least 15 million, maybe even 70 million years,” says Professor Ebert. What is particularly astonishing is that this process took place without interruption, even though living conditions on Earth have changed dramatically several times during this period. “We’re not talking about a temperature difference of one or two degrees, but fluctuations of more than 10 degrees, including multiple ice ages.” The process may even have survived the meteor impact which is blamed for the extinction of the dinosaurs.
The research team used three different species of water fleas collected from natural populations in North America, Africa, Europe and Asia. Phylogenetic analysis showed that these species split off at least 15 million years ago. Nevertheless, they were all susceptible to the same parasitic bacterium.
The researchers then found several sections in the water flea’s genetic material that encoded components of the immune system and exhibited a high degree of variability. This diversity allows the water flea to keep denying the parasite access. Surprisingly, these variable regions were found in the same sections of genetic material in all water flea species. This shows that the coevolution between water fleas and the parasite began before the host species split off, at least 15 million years ago. It also means that this process was uninterrupted – because interruption would mean genetic variants would be lost in a relatively short time.
Lower variability, greater susceptibility to infections
“We tend to think that evolution is always inventing something new. Here, we were able to show that the same variants of genes were used again and again over vast periods of time,” says Ebert. In humans, too, genetic variation ensure a flexible immune system − for example, in the “histocompatibility complex”, which recognizes and combats foreign structures. However, no one had managed to trace these processes very far back. And in contrast to the water flea, it appears to involve multiple pathogens. “Genetic diversity offers protection against infectious diseases, including new diseases. That’s why it’s so important to understand how this variability is maintained over long periods of time,” says the evolutionary biologist.
Originalpublikation
Luca Cornetti, Peter D. Fields, Louis Du Pasquier und Dieter Ebert
Long-term balancing selection for pathogen resistance maintains trans-species polymorphisms in a planktonic crustacean.
Nature Communications (2024), doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49726-8