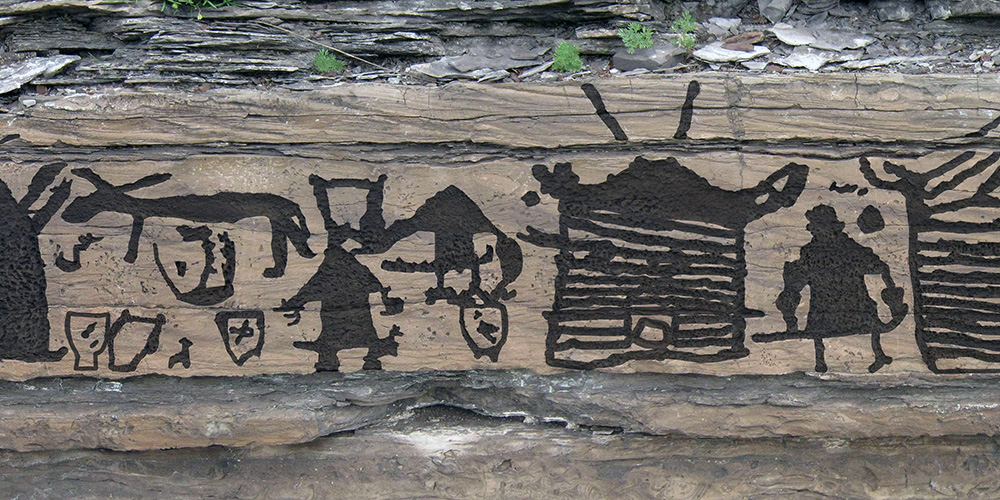
Bronze cauldrons were used by the inhabitants of the Mongolian steppe around 2,700 years ago to process animal blood and milk. This is shown by a protein analysis of archaeological finds from this period.

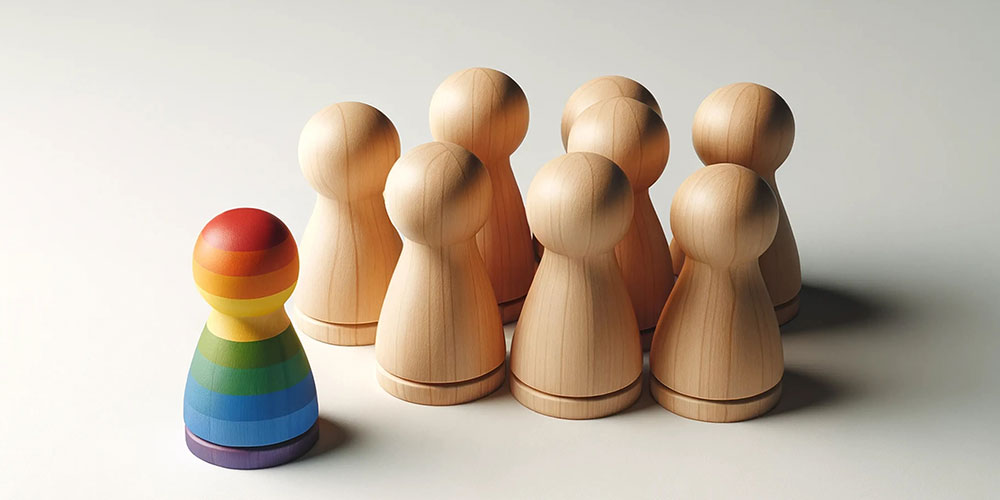
Lesbian, gay and bisexual people experience greater exclusion than heterosexual people. This is the conclusion of a recent study by researchers from the University of Basel and the University of Kaiserslautern-Landau (RPTU). Heterosexual individuals who deviate from traditional gender roles are also affected.

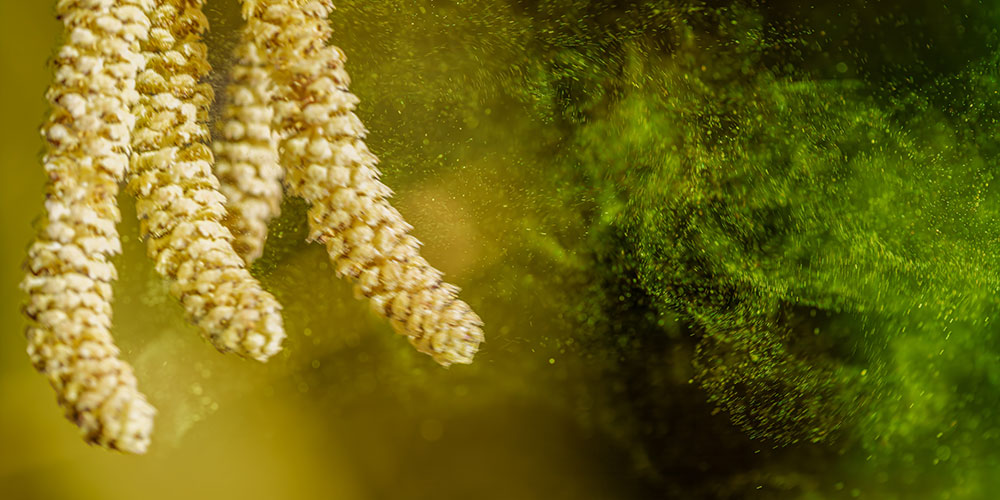
An estimated one-fifth of the world's population is affected by pollen allergies. Researchers at Swiss TPH and the University of Basel have now discovered that a high concentration of pollen can increase blood pressure in allergy sufferers.

The Epstein-Barr virus can cause a spectrum of diseases, including a range of cancers. Emerging data now show that inhibition of a specific metabolic pathway in infected cells can diminish latent infection and therefore the risk of downstream disease, as reported by researchers from the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel in the journal Science.
Researchers have developed an approach to “deleting” a blood system affected by leukemia while simultaneously building up a new, healthy system with donor blood stem cells. Writing in the journal Nature, the team reports on the promising results obtained in animal experiments and with human cells in the laboratory.
When cells become tumor cells, their metabolism changes fundamentally. Researchers at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel have now demonstrated that this change leaves traces that could provide targets for cancer immunotherapies.
Researchers at the University of Basel have developed a new method for calculating phase diagrams of physical systems that works similarly to ChatGPT. This artificial intelligence could even automate scientific experiments in the future.

Researchers from Switzerland, France, Germany and Luxembourg plan to use artificial intelligence to improve the treatment of patients with autoimmune diseases. The aim is to enable customized therapies for multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel conditions.

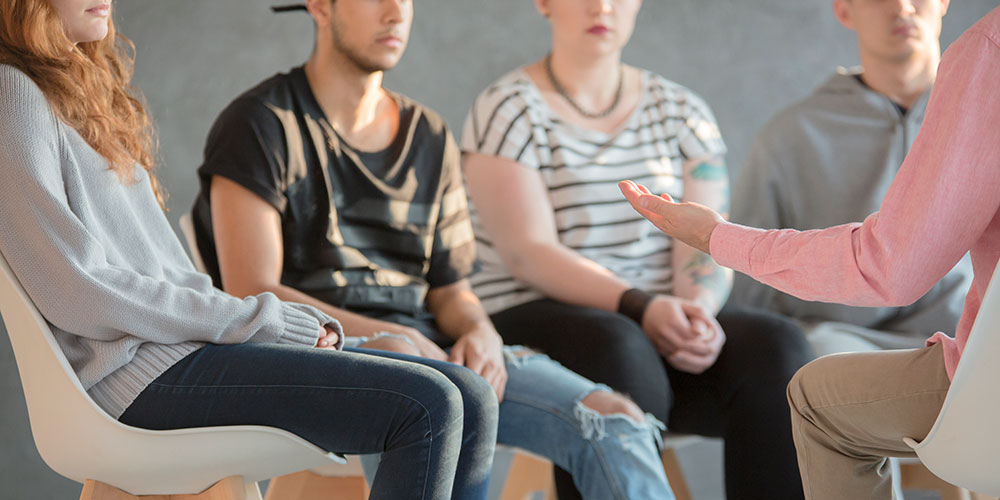
Whenever a child behaves aggressively at school, a lack of parenting is often assumed. This overlooks the possibility of underlying mental health problems. Through a new type of training program, researchers at the University of Basel are attempting to train young people to better cope with stress and strong emotions.